| <<Prev |
graphical
editor -- Visual
C# .NET / CSharp Example Source Code! |
|
| Graphics
Libraries and SDK Tools
for programmers and developers! |
The
VC++ source codes of this tool is shipped with E-XD++
Library Enterprise Edition, order it now.
It is the world leading
graphical
component, and
graphical tool / graphical drawing tool.
It
ships with 100% full VC++ and VC#
Source
Codes
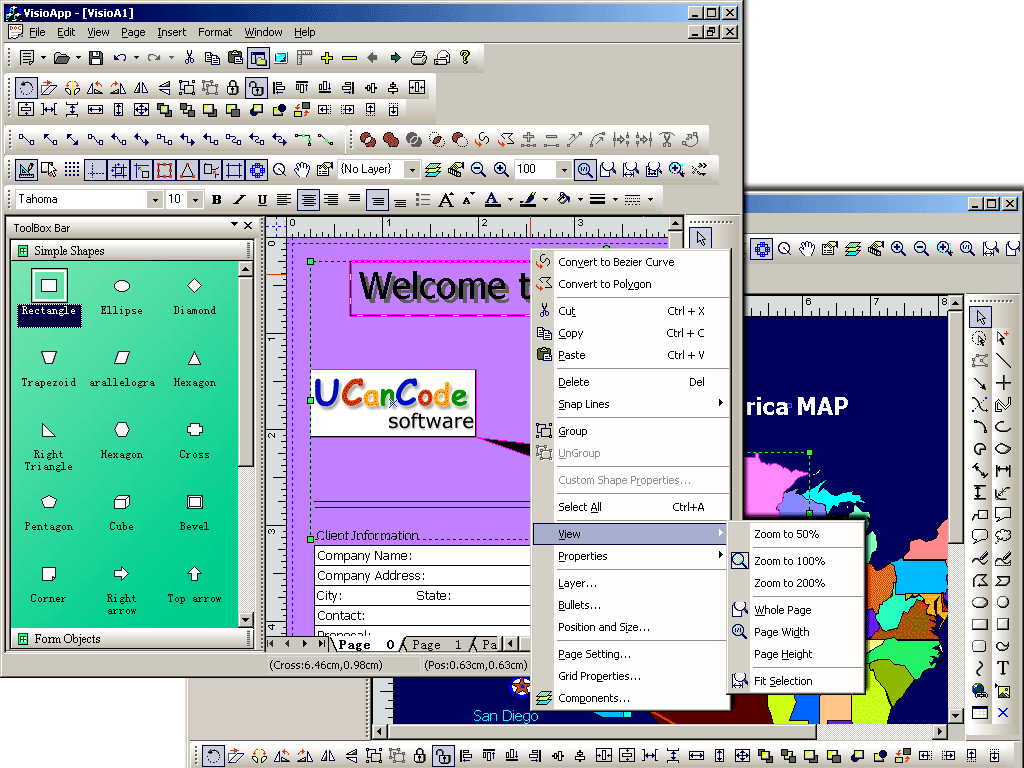
A graphical editor integrated in
Visual Studio .NET. Design graphics in the Picture
Designer the same way you design
application: without writing code.
Graphical objects: rectangles, rounded rectangles, ellipses, arcs, pies, polygons, polylines, splines, paths, images, text, and Groups.
Automatic screen updates simplify runtime animation. Change an object property, and
XD++ updates the screen, intelligently repairing overlapping objects.
Maximum performance: XD++ batches screen updates, repainting a minimum number of pixels. Tweak the performance of any Element by changing anti-aliasing or gamma-correction with a RenderAppearance.
It includes C# Example
and C# Tutorial, and tons of other C#
Source Code.
C#
Tutorial:
A
gauge control with all source code, .net 2.0
Call JavaScript
from Visual
C++ and MFC, Article and Example
C# Example: Free Draw .NET GDI+
Gauge Control with Source
Code
C# Tutorial For
Beginners
So you just install .NET
framework and want to start using C# but
you don't know where to start ? well...
First you could download this complete tutorial
here. There is a directory for each tutorial with a
build.bat to build the tutorial and a run.bat to run the program.
And every example is already compiled, just in case...
UCCDraw
ActiveX Control is an ActiveX control that
allows creation and editing of Visio-style charts
from within your application. Allows you to create
flow charts, vector drawings, raster images and
more with the ability to include hyperlinks and
various shading and coloring effects. You can
group objects together, include images and text,
link them together and apply custom drawing
effects to create charts similar to Microsoft
Visio, Adobe Illustrator, and CorelDRAW
 >>
>>
UCanCode's Flow Diagramming
Source Code Kit
C#
Solution Can be found
here
First tutorial
You should first open a DOS command shell. (If
you don't know what it is, clic on the Start menu then run (at the
bottom) and type, in the text field: "cmd".
exercise: there is an easiest way to do that, try to find it.)
You should begin to work in an empty directory for this. let call it "C:\learncs".
Type in the shell:
> md C:\learncs
> cd C:\learncs
> C:
Now you should create your first C#
program, type "notepad hello.cs" and type (in the
notepad)
using System;
public class Hello
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello C# World :-)");
}
}
the
using keyword just let you write
Console
at line 7, instead of
System.Console. It's very usefull shortcut when
you use a lot of "class" define in System.
Save the file.
Now you could compile. Type in the DOS Shell again and type:
csc /nologo /out:hello.exe hello.cs
You probaly have some errors, correct them, compile again, and now you have a
working hello.exe program... type
hello, see...
Second tutorial
Congratulation you've done the most
difficult, let increase the difficulty. and create an object instance. in the
DOS shell create a new directory:
> md ..\learncs2
> cd ..\learncs2
> notepad hello.cs
and then type, in the notepad
using System;
public class Echo
{
string myString;
public Echo(string aString)
{
myString = aString;
}
public void Tell()
{
Console.WriteLine(myString);
}
}
public class Hello
{
public static void Main()
{
Echo h = new Echo("Hello my 1st C# object !");
h.Tell();
}
}
Wouah, 25 lines! That's a program! Save it,
compile it, run it...
What happened? csc look for a Main() function in your program, it should
find one (and only one) and it will be the entry point of your program.
In this tutorial we create 2 classes: Echo & Hello. In the Main() method you
create an Echo object (an instance of the Echo class) with the keyword new
Then we called the instance method "Tell()".
the upper case letter on class or Method is just a MS convention, do as it
pleased you.
public is a visibility access, method wich are not public could not be seen from
outside, there is also other visibility keywords, to learn more, clic on Start
menu-> Programs -> Microsoft .NET Framework SDK -> Documentation
there is a search window, an index window, etc... try to learn more about public
private protected.
Third tutorial
Now you become to be pretty confident, I guess, so
we could start using multiple file, and even a dll ? go into an other directory
(or stay in this one, I won't mind) and create 2 file:
hello.cs
using System;
public class Hello
{
public static void Main()
{
HelloUtil.Echo h = new HelloUtil.Echo("Hello my 1st C# object !");
h.Tell();
}
}
echo.cs
using System;
namespace HelloUtil
{
public class Echo
{
string myString;
public Echo(string aString)
{
myString = aString;
}
public void Tell()
{
Console.WriteLine(myString);
}
}
}
Note in hello.cs I have used the syntax "HelloUtil.Echo"
it's because
Echo is in the namespace
HelloUtil, you could
have typed (at he start of the file)
using HelloUtil and avoid
HelloUtil.,
that's the way namespace work.
Now you could compile both in one .exe with
> csc /nologo /out:hello.exe *.cs
But it's not my intention, no.
Well.
(Have you tried?)
Let's go building a DLL:
> csc /nologo /t:library /out:echo.dll echo.cs
that's it (dir will confirm).
Now we could use it ...
> csc /out:hello.exe /r:echo.dll hello.cs
if you typed "hello" it will worked as usual..., but if you delete
"echo.dll" the program will now crash: it use the DLL. You could also
change Echo.cs, rebuild the DLL and see... that's the advantage of DLL!
You could also put your DLL in the global
assembly cache (GAC), and any program would be able to access it, even if the
DLL is not in its directory!
to put it in the GAC, I sugest you read MS doc but here are the unexplained
step:
- create your assembly key, create it once and
use it for every version. you create it with:
sn -k myKeyName.snk
the .snk file should be in your compilation directory (the one where your
run csc)
- create a strong asssembly title by adding in
any .cs source file the following directive at top level:
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
[assembly: AssemblyTitle("My Lib Title")]
[assembly: AssemblyVersion("1.2.3.4")]
[assembly: AssemblyKeyFile("myKeyName.snk")]
- now add it to the GAC:
> gacutil.exe /if myLib.dll
By the way, did I tell you ? when I referenced
the hello.dll while compiling, remember?
csc /out:hello.exe /r:echo.dll
hello.cs, it could have been any assembly, even a .exe !!!
Fourth tutorial
Congratulation you would soon be able to
hack CsGL but there is one last step
you should understand : interop (with C code).
You will need a C compiler, I advise gcc for windows called MinGW,
it's free, it's good, it's GCC!
We will create 3 file:
echo.c
#include <stdio.h>
#define DLLOBJECT __declspec(dllexport)
DLLOBJECT void writeln(char* s)
{
printf("%s\n", s);
}
echo.cs
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace HelloUtil
{
public class Echo
{
[DllImport("echo.native.dll", CallingConvention=CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
static extern void writeln(string s);
string myString;
public Echo(string aString)
{
myString = aString;
}
public void Tell()
{
writeln(myString);
}
}
}
hello.cs
using System;
using HelloUtil;
public class Hello
{
public static void Main()
{
Echo h = new Echo("Hello my 1st interop code !");
h.Tell();
}
}
Hehe, here you discover a completly new thing,
Attribute.
"[DllImport(.." is an attribute.
You could tag any method/field/class with any number of attribute.
They generate extra information that could be used by anyone who could
understand them.
This DllImport attribute is understand by the compiler and told him that the
function below is in fact in a DLL whose name is "echo.native.dll". I
add a calling convention parameter as the default .NET calling convention is __stdcall
whereas, in C, it's __cdecl.
By the way, if you look for DllImport in the documentation, look for DllImportAttribute,
because you remove "Attribute" to attribute classname when using them,
it's like this.
And now let's compile this!
> csc /nologo /t:library /out:echo.dll echo.cs
> csc /nologo /out:hello.exe /r:echo.dll hello.cs
>
> rem "if the following line don't work, read bellow.."
> gcc -shared -o echo.native.dll echo.c
> strip echo.native.dll
the 2 last line (the
gcc & strip
command) are for building the "C-DLL".
If they don't work maybe gcc is not in a directory listed in your path
environment variable ? check with:
%lt; echo %PATH%
Well it's probably not,anyway, so type, assumin mingc is in C:\MinGW:
set PATH=C:\MinGW;%PATH%
And try again... you sure it's not a syntax error ?
If it compile test it now:
hello
Great isn't it ?
Now I should admit I didn't tell you all the
truth.
echo.dll and
echo.native.dll are not the same kind of
DLL. It's not just the language (C / C#) the
C one is a plain executable full of, probably, x86 instruction, whereas the C#
one is what MS call a portable executable.. anyway they are different.
If you install echo.dll in the GAC it wont work because it won't find
echo.native.dll except if you put in into the PATH (like C:\Windows\System32).
In the same manner when you add the reference in VS.NET
echo.native.dll is overlooked and your program won't work....
So either put the native one in your path or copy it in the debug/release
directory of VS.NET.
Or do everything by hand (makefile? build.bat?) and put all your dll in you
build directory, and everything work fine..
And now..
Well, first forget about notepad. It's good to
learn, but so painfull to use regularly.., try to find real developer friendly
small text editor (like JFE)
or a complete IDE like SharpDevelop.
Now you are ready to understand, I could tell
you all the truth:
csgl.dll is a C# assembly and
csgl.native.dll
is just a dll compiled by GCC, upon which csgl.dll depends...
 Get
Business Card / Label
Print Component
C++ Source Codes
Get
Business Card / Label
Print Component
C++ Source Codes
 Using
GDI+
with
MFC or native C/VC++
Using
GDI+
with
MFC or native C/VC++
 Introduction to GDI+ in
.NET
Introduction to GDI+ in
.NET
 GDI+ Font,
Brush
and
Bitmap
GDI+ Font,
Brush
and
Bitmap
 GDI+ GraphicsPath
and
LinearGradientBrush
GDI+ GraphicsPath
and
LinearGradientBrush
 GDI+ Printing.
GDI+ Printing.
 GDI+
and
DrawArc
and
DrawPath
GDI+
and
DrawArc
and
DrawPath
 High-speed Charting Control, Real Time Chart,
Data Visualization, C# Source Code
High-speed Charting Control, Real Time Chart,
Data Visualization, C# Source Code
 Date-Time Edit Control
A simple mucancode.neted
date-time editor. VC++
Article Source Code
and
GetWindowText
Date-Time Edit Control
A simple mucancode.neted
date-time editor. VC++
Article Source Code
and
GetWindowText
 VC++ MFC Project Setting, Unicode,
MBCS,_MBCS
or
_UNICODE,
VC++ MFC Project Setting, Unicode,
MBCS,_MBCS
or
_UNICODE,
wWinMainCRTStartup
 Screen Capture , to Clipboard, C++ Source Code,
Get bitmap of Window
Screen Capture , to Clipboard, C++ Source Code,
Get bitmap of Window
 Draw, Print and encode UPCA barcode
and UPCE barcode, and EAN13 barcode
with VC++ Codes
Draw, Print and encode UPCA barcode
and UPCE barcode, and EAN13 barcode
with VC++ Codes
 VC++
Sample:
Multiple Views layout of
RepositionBars and DeferWindowPos with
RecalcLayout and UpdateAllViews
VC++
Sample:
Multiple Views layout of
RepositionBars and DeferWindowPos with
RecalcLayout and UpdateAllViews
 GDI+ Color
and
ARGB
with
Example
GDI+ Color
and
ARGB
with
Example
 .NET
HMI & SCADA Solution.
.NET
HMI & SCADA Solution.
 VC++
Ado Tutorial
with VC++ Ado Sample and VC++ Ado Example
VC++
Ado Tutorial
with VC++ Ado Sample and VC++ Ado Example
 Converter
Convert RTF to HTML
with VC++ Source Codes, and
RICHED32.DLL
Converter
Convert RTF to HTML
with VC++ Source Codes, and
RICHED32.DLL
 Add proto - logic diagram displays to your
Java, C++, and .NET applications, for the desktop and rich
internet applications.
Add proto - logic diagram displays to your
Java, C++, and .NET applications, for the desktop and rich
internet applications.
 CAM
simulator
Sample with
VC++ MFC Source Code
CAM
simulator
Sample with
VC++ MFC Source Code
 CDialogBar,
CBitmapButton in Dialog Bar, SubclassDlgItem and EnableDocking
VC++ Example
CDialogBar,
CBitmapButton in Dialog Bar, SubclassDlgItem and EnableDocking
VC++ Example
 MFC Sample Code: Load and Display
PNG Image File
MFC Sample Code: Load and Display
PNG Image File
 VC++ Example
Capture Print Screen to
Clipboard including
dropdown menu,
SetWindowsHookEx
and
UnhookWindowsHookEx,
with
RegisterWindowMessage
VC++ Example
Capture Print Screen to
Clipboard including
dropdown menu,
SetWindowsHookEx
and
UnhookWindowsHookEx,
with
RegisterWindowMessage
 UML
Diagram Component / Drawing C++ Source Code Solution
from UCanCode,
it will save you 50% - 80% time for building any UML based application.
UML
Diagram Component / Drawing C++ Source Code Solution
from UCanCode,
it will save you 50% - 80% time for building any UML based application.
 VC++
XML Read and Write Article: C++ Source Code for
Creating and Processing XML documents
VC++
XML Read and Write Article: C++ Source Code for
Creating and Processing XML documents
 VC++
Article: CSplitterWnd Extension that
Allows Create Multiple Views, and
Switch Views in Any Pane
VC++
Article: CSplitterWnd Extension that
Allows Create Multiple Views, and
Switch Views in Any Pane
News:
1 UCanCode Advance E-XD++
CAD Drawing and Printing Solution
Source Code Solution for C/C++, .NET V2025 is released!
2
UCanCode Advance E-XD++
HMI & SCADA Source Code Solution for C/C++, .NET V2025 is released!
3
UCanCode
Advance E-XD++ GIS SVG Drawing and Printing Solution
Source Code Solution for C/C++, .NET V2025 is released!
Contact UCanCode Software
To buy the source code or learn more about with: